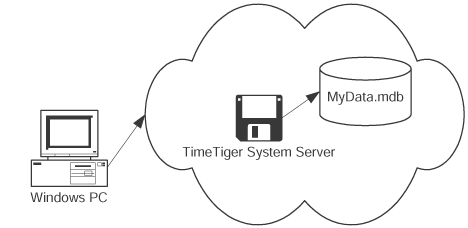
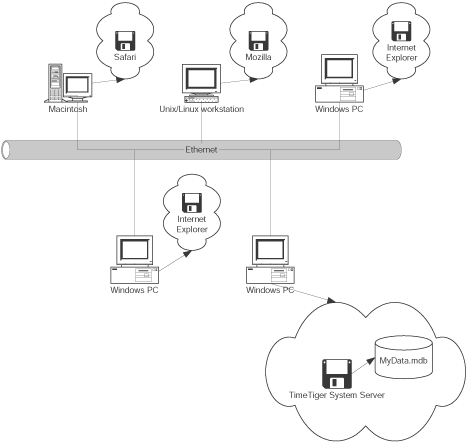
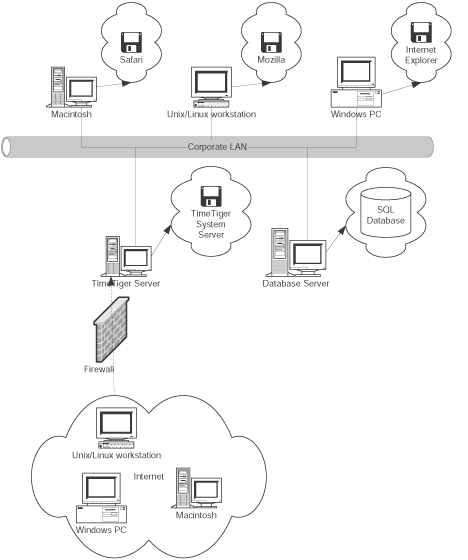
The services offered to Departments will cover new network installations, network upgrades, troubleshooting, and maintenance. We provide:
· Network needs assessment
· Software and hardware support for most available LAN systems and LAN based software packages
· Network installation and upgrades
· Network troubleshooting
New LANs
For new network installations, our staff can assist with network needs analysis; prepare or review specs for new networks or network upgrades; install/upgrade network operating system on network server; install, connect, and configure workstations and peripherals, and install, upgrade and configure network software applications.
LAN Upgrades
Network upgrades, including the upgrade of network operating system software; the installation and configuration of new network applications; the installation, connection, and configuration of additional workstations and peripherals; and the installation and configuration of hardware upgrades in network servers, are all a part of this new service. In addition, our staff can help coordinate LAN connections with the campus-wide network (when available).
Trouble Shooting & Problem Solving
We can troubleshoot network problems involving operating systems, the server, workstations, network applications, and printing. Network maintenance can also be provided including maintaining network documentation, remote network monitoring, optimizing server performance, design and help maintain network backup schedule, and installation of network operating system upgrades and fixes. Our staff can also design and/or conduct seminars for network managers and for network users as a non-contract service.

Network Maintence:
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is one of the most ignored aspects of network ownership. Preventive Maintenance refers to performing proactive maintenance in order to prevent system problems. This is different from diagnostic or corrective maintenance, which is performed to correct an
already-existing problem. Here are some reasons why you should develop a preventive maintenance plan for your network:
1. Preventive Maintenance Saves Money: Avoiding problems with your PC will save you money in the long run. By preventing a problem from occurring, you will no longer need to spend money on new components or repair jobs.
2. Preventive Maintenance Saves Time: Preventive maintenance saves time because it saves you the inconvenience and disruption of system failures and lost data. Most preventive maintenance procedures are quite simple compared to troubleshooting and repair procedures.
3. Preventive Maintenance Helps Safeguard Your Data: For most people, the data on the hard disk is more important than the hardware that houses it. Taking steps to protect this data therefore makes sense, and that is what preventative maintenance is all about.
4.Preventive Maintenance Improves Performance: Some parts of your system will actually degrade in performance over time, and preventive maintenance will help to improve the speed of your system in these respects. It is important to us at Dapoy that your computer systems will be as
secure and steady as possible. If you would like to get an estimate for preventive maintenance that will suit your business needs, please contact the office to speak to a technical representative today.
Cabling and Infrastructure :
Network Performance
The performance of a network infrastructure depends not only on the quality of its components, but also on the quality of the cabling installation. Each network infrastructure is installed and tested by trained quality assurance engineers and technicians.
A properly installed cable network should function efficiently for 10-12 years. We guarantee all of our cabling installation for up to 12 years.